Within the Microsoft Exchange Transport Service, a feature known as categories determines what is to be done with an email when it is routed to a route destination. Route destinations can be labeled as any of the following group types:
Routable DAG: 2013 mailbox that belongs to a delivery group boundary.
Mail Delivery Group: Collection of Exchange server under 1 site.
Connection Source Servers: A send connector directed to a specific location.
AD Site: HUB AD site.
Server List: Distribution or mailing list.
Exchange 2013 is site aware; it uses the AD topology service to determine the IP subnet and border or neighbor devices. To determine the email delivery, Exchange 2013 uses a least-cost routing IP Site Links mechanism that can detect the speed, bandwidth and reliability of a route. If Exchange 2013 is installed on multiple sites, it will use the least costly site to route email as indicated in the diagram below.
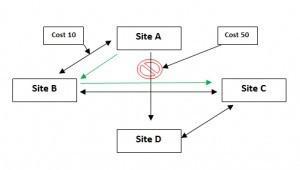
You can use the Exchange Management Shell or the EMS to assign cost value between sites and set the maximum message size quota limit between sites as well. This will allow fewer bottlenecks and also improve email production on mail delivery. The command-lets are listed below.
PS: Set-ADSiteLink Assigns cost value between site and also sets maximum message size.
PS: SetADSite To force mail flow for one site to another.




Leave a Comment