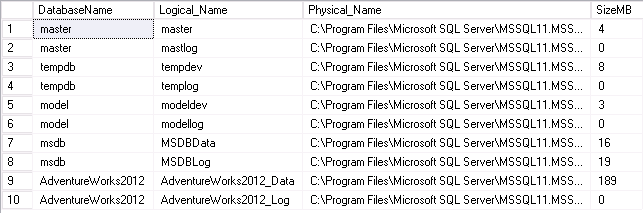
There are a few ways to get the size of databases within SQL Server without the need of right clicking the DB and selecting the Properties option.
We can use the classic T-SQL query directly from the SQL Server Management Studio to display all the DBs and their sizes.
SELECT DB_NAME(database_id) AS DatabaseName,
Name AS Logical_Name,
Physical_Name, (size*8)/1024 SizeMB
FROM sys.master_files
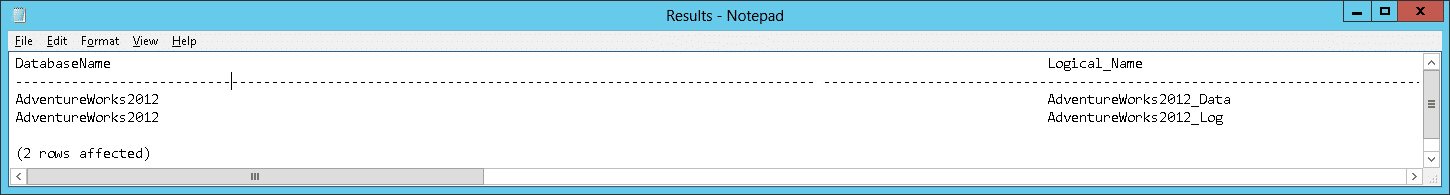
Or if just add a “Where” statement filter at the end to retrieve only one DB
SELECT DB_NAME(database_id) AS DatabaseName,
Name AS Logical_Name,
Physical_Name, (size*8)/1024 SizeMB
FROM sys.master_files
WHERE DB_NAME(database_id) = ‘AdventureWorks2012’

There is also another method if you have no access to the Management Studio or just prefer the Command line. You can use the SQLCMD command (Program FilesMicrosoft SQL Server110ToolsBinn>)
The command tool can get quite complex depending on the task you want to perform, but in this case we will be simply calling up a query file and export the results to a text file.
The SQLCMD tool can be used to get information from a SQL server in a verbose way without access the GUI.
So to start, one can simply go to the path mentioned above and type the command in the Command Prompt window (sqlcmd -S localhost -i C:ScriptsDBsize.sql)
Before you must have a SQL file that is ready with a query in order to get the information. So when you write the command you have to mention the server name (-S), UserName and Password, and the path of the file (-i)
As soon as you press enter, the results will get displayed on the screen. This is fine to get a quick visual, but if you want a physical copy of the results, just add the name of the file you want the results to be saved.
This can be added to the end of the command using the (-o) switch and the path
sqlcmd -S localhost -i C:ScriptsDBsize.sql -o C:ScriptsResults.txt