There are several ways to configure a spam filter with Exchange Serverâ„¢.
Method 1: Place the spam filter in the DMZ
With this method, the spam filter resides in the DMZ while the Exchange Server and other network resources are protected behind a firewall.
The way the DMZ is configured can vary. Some clients set up two firewalls and create a separate subnet for the DMZ while others have the DMZ function built into the firewalls.
Method 2: Place the spam filter on the same subnet as Exchange
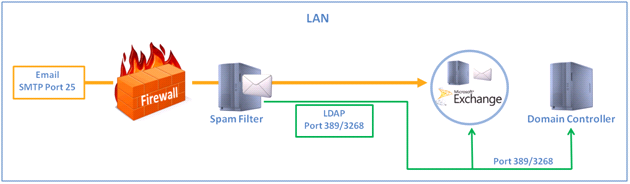 With this setup, the firewall provides Network Address Translation (NAT) or simple port filtering. However, the firewall is usually configured to carry out port forwarding to the Exchange Server. This is an easy configuration with which to work as you can integrate your spam filter into the network, test the configuration in a parallel state and, with a simple change in the NAT rule, route mail to the spam Filter.
With this setup, the firewall provides Network Address Translation (NAT) or simple port filtering. However, the firewall is usually configured to carry out port forwarding to the Exchange Server. This is an easy configuration with which to work as you can integrate your spam filter into the network, test the configuration in a parallel state and, with a simple change in the NAT rule, route mail to the spam Filter.
This diagram is meant to be a general representation of the way this network would be deployed:
Method 3: Spam filter installed on the Exchange Server
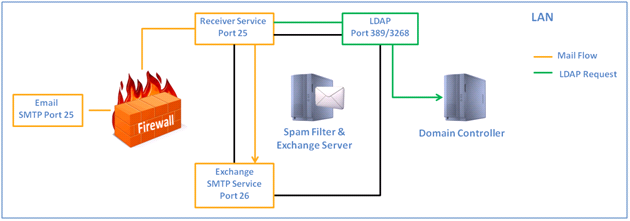 This deployment scenario is the least recommended because of the load on system resources. However it is possible to use this type of deployment if there is a lack of hardware, or if there is a relatively small number of mailboxes in use and/or there is very little traffic.
This deployment scenario is the least recommended because of the load on system resources. However it is possible to use this type of deployment if there is a lack of hardware, or if there is a relatively small number of mailboxes in use and/or there is very little traffic.




